Today i will show you that how can you use input command in python language, so we will write a simple program that will ask for any name or value and then print that name or value.
So here is our simple program.
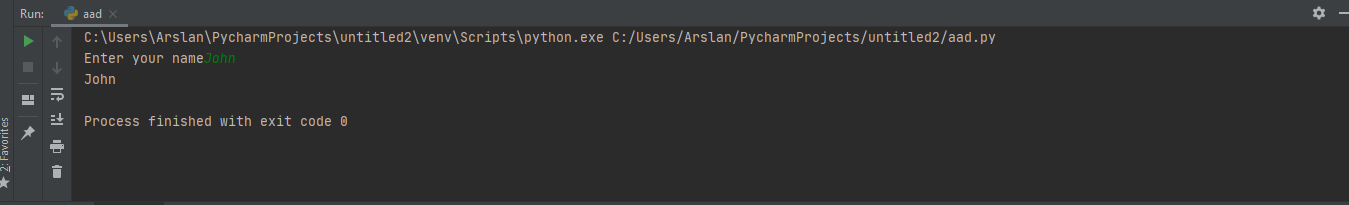
a=input("Enter your name")
print(a)
as you can see we have declared "a" a variable that will ask for input "Enter your name" and then print command will print the variable "a". So anything we will type will be printed. As show in the picture below.
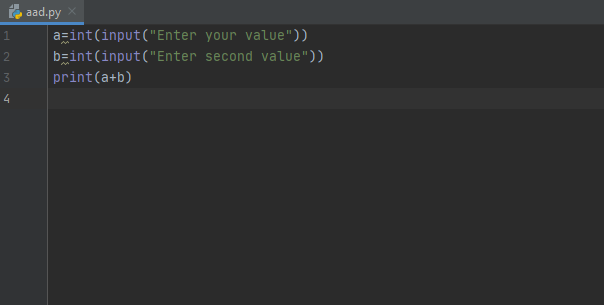
But here you have to remember, if you are working with integers for some mathematical work than you have to declare input type as integer because then python will take input type as integer and not as word. As show in the picture below.
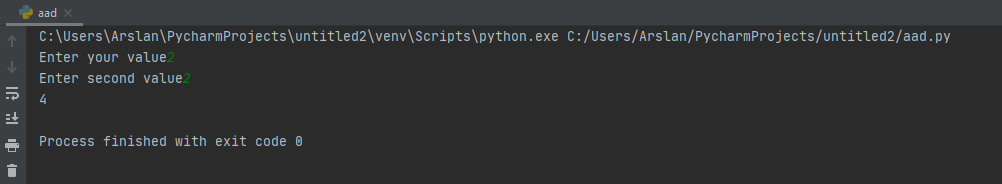
As you can see the syntax that how can we declaring the input type,,int, we have to write int then in brackets we have to enter the input command, int stands for integer and it will declare our input as integer, we have and in print command we have instructed to add a+b, so our program will add both entered values of a and b. Now see its output in the image below
This is the output that we will get of the above code, it is asking for two integers and then adding them
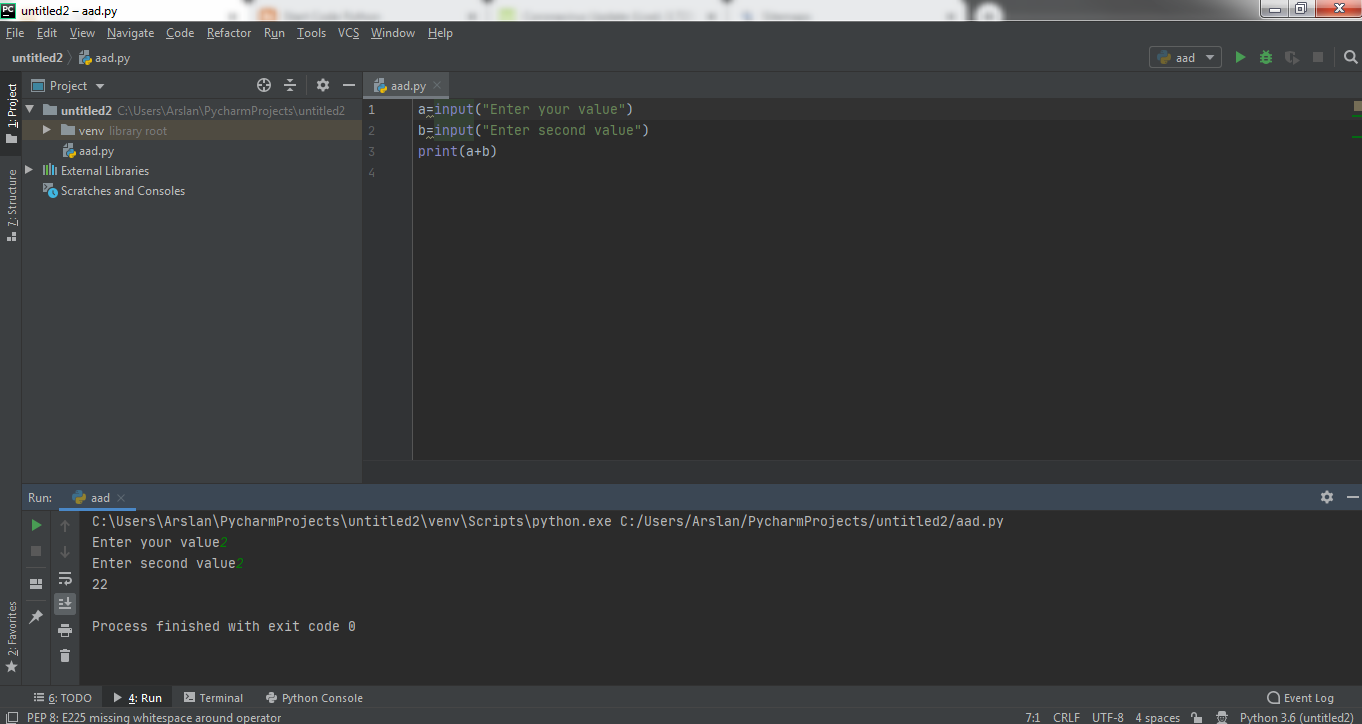
If we don't declare our input as integer then python will not take our input as integer rather treat it as a word and will simply give us output 22 instead of 4 because our values will be treated as words and our command print(a+b) will just write them both of these values together instead of performing any arithmetic calculations. Kindly see the image below to get better understanding of it.

Comments
Post a Comment