We are going to write code for a simple calculator in python, It will show you that how can you use basic python statements and function to make a calculator that will do addition, subtraction,multiplication and division.
Calculator python coding:
def add(a, b):
return a + b
def subtract(a, b):
return a - b
def multiply(a, b):
return a * b
def divide(a, b):
return a / b
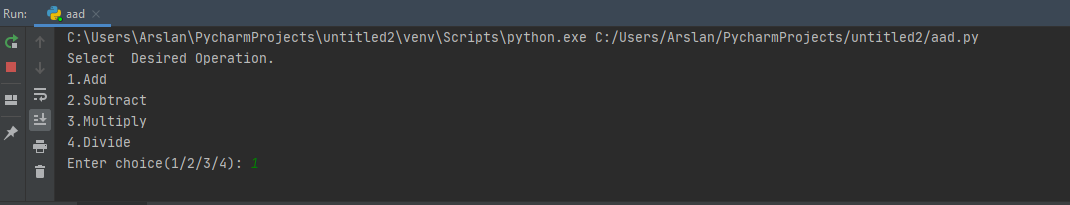
print("Select Desired Operation.")
print("1.Add")
print("2.Subtract")
print("3.Multiply")
print("4.Divide")
while True:
choice = input("Enter choice(1/2/3/4): ")
if choice in ('1', '2', '3', '4'):
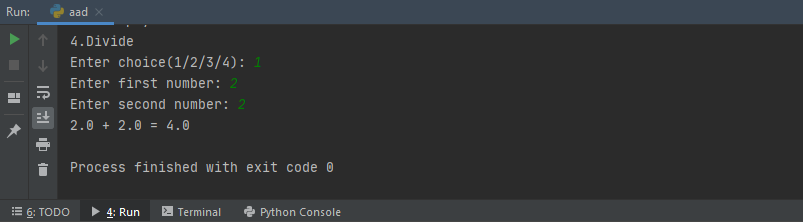
num1 = float(input("Enter first number: "))
num2 = float(input("Enter second number: "))
if choice == '1':
print(num1, "+", num2, "=", add(num1, num2))
elif choice == '2':
print(num1, "-", num2, "=", subtract(num1, num2))
elif choice == '3':
print(num1, "*", num2, "=", multiply(num1, num2))
elif choice == '4':
print(num1, "/", num2, "=", divide(num1, num2))
break
else:
print("Invalid Input")
Now lets break down the code to get better understanding of it.First of all we have to define function for addition,subtraction,multiplication and division.
def add(a, b):
return a + b
def subtract(a, b):
return a - b
def multiply(a, b):
return a * b
def divide(a, b):
return a / b
In the above portion we have defined all the functions because in python we don't have option to use goto or jump statements as in other languages such as c++. So we have to manually define each of these as function with return statement and refer these return statement whenever we use in our code.
Now come to second part.
print("Select Desired Operation.")
print("1.Add")
print("2.Subtract")
print("3.Multiply")
print("4.Divide")
In this portion we have used print statements that will execute first and show the option of the code that which option we want to use to perform arithmetic work.
Now Final part of the program
while True:
choice = input("Enter choice(1/2/3/4): ")
if choice in ('1', '2', '3', '4'):
num1 = float(input("Enter first number: "))
num2 = float(input("Enter second number: "))
if choice == '1':
print(num1, "+", num2, "=", add(num1, num2))
elif choice == '2':
print(num1, "-", num2, "=", subtract(num1, num2))
elif choice == '3':
print(num1, "*", num2, "=", multiply(num1, num2))
elif choice == '4':
print(num1, "/", num2, "=", divide(num1, num2))
break
else:
print("Invalid Input")
Now this is final part of our program and that most important part which will perform the functions in calculator. In this part first of all we have used while statement which will check if the entered value or condition is true.
Then we will define the conditions by using if and elif statements. First we have declared a choice variable that will ask for input that what arthimatic function we want to perform e.g addition, subtration etc.
Then we have used If statement to check for the enter value whether entered value range between 1-4, then it will ask for first and second number,which we have written in the program and in program we have declared data type as float(float data type will show numbers as 2.0,3.0,4.0) and then used if and elif statements and recalled the already defined function in the start of the code.
If entered value is other than 1-4 then it will show invalid option as Else statement is used in the end of program with "Invalid input" option.
The output of this code is show below:

Comments
Post a Comment